iOS 17.4’s iMessage with PQ3 Makes it the Most Secure Messaging Platform Ever

Apple’s iMessage has long been a leader in end-to-end encryption, making secure communication accessible to millions of users worldwide. With the introduction of PQ3, iMessage raises the bar even higher, becoming the first major messaging platform to achieve Level 3 security. This groundbreaking cryptographic protocol offers unparalleled protection against current threats and prepares iMessage to withstand the potential of future quantum computers.
The Quantum Threat
Classical cryptography, which underpins most of our digital security, relies on mathematical problems that are difficult for today’s computers to solve. But quantum computers, with their fundamentally different way of computing, could break these algorithms. While practical quantum computers capable of this may be years away, attackers could start collecting encrypted data now and decrypt it later with quantum technology—a strategy known as “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later.”
Post-Quantum Cryptography to the Rescue
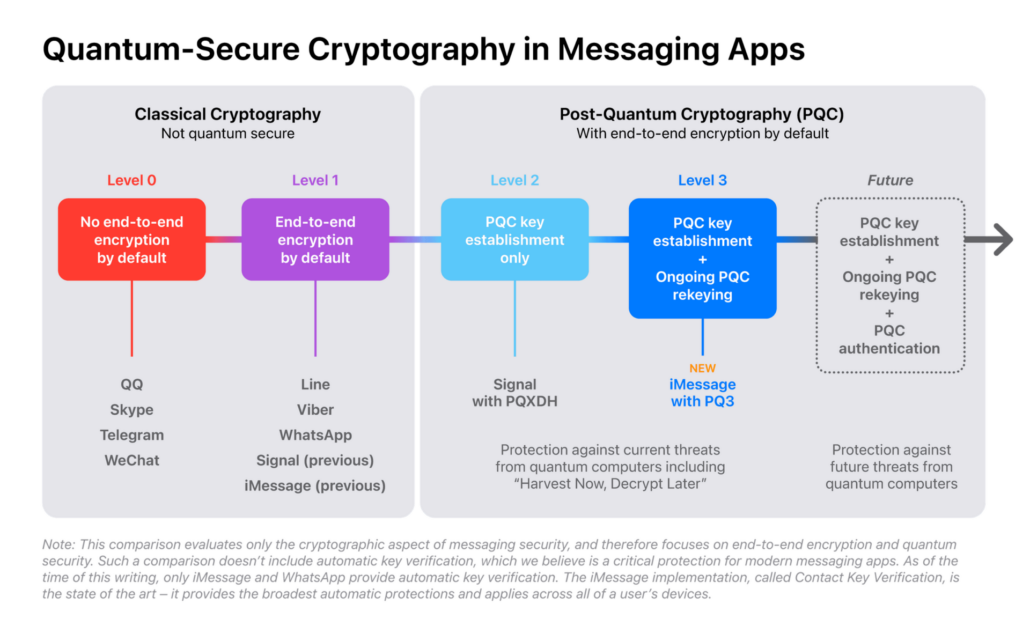
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is a field focused on algorithms designed to be secure even with a quantum computer. By incorporating PQC, messaging apps can move towards higher security levels. Currently, most messaging services are at Level 0 (no end-to-end encryption) or Level 1 (basic encryption vulnerable to key compromise). Signal recently reached Level 2 by adding some post-quantum security.
PQ3: Level 3 Security
iMessage’s PQ3 protocol is revolutionary. It secures the entire conversation with quantum-resistant technology, from initial setup to every single message. It includes a post-quantum “self-healing” mechanism: even if encryption keys are compromised, their impact is limited, ensuring that ongoing communication remains protected.
PQ3’s Design
To achieve its remarkable defense, PQ3 meticulously follows these principles:
- Quantum-resistance from the start: PQ3 uses the Kyber algorithm for quantum-safe key exchange during initial setup.
- Key compromise resilience: Frequent key rekeying limits the damage of key breaches.
- Hybrid approach: PQ3 combines post-quantum and battle-tested elliptic curve cryptography for maximum security.
- Message size management: Smart design minimizes the overhead of post-quantum encryption.
- Rigorous verification: PQ3’s security has been mathematically proven by independent experts.
Formal Proof: Confidence in PQ3
Leading cryptographers have thoroughly analyzed PQ3. Professor Douglas Stebila focused on game-based proofs, while Professor David Basin’s team used symbolic evaluation. Both analyses confirm that PQ3’s security relies on the underlying algorithms being secure, providing strong guarantees against both classical and quantum attacks.
PQ3: A Deep Dive
Let’s explore PQ3’s inner workings to fully appreciate its innovation:
Post-Quantum Key Establishment
- Registration: Each iMessage device creates multiple keys: a post-quantum Kyber key, a classical elliptic curve (P-256) key, and an ECDSA authentication key (also P-256). These public keys are sent to Apple’s servers (IDS) for other devices to access during communication.
- Initial Exchange: When you start a new chat, your device fetches the recipient’s keys. It uses classical ECDH with their elliptic curve key and post-quantum Kyber encapsulation with their Kyber key to create two shared secrets.
- Hybrid Derivation: The two secrets are combined in a way that makes breaking either one necessary to compromise the session, ensuring the highest security.
Post-Quantum Rekeying
PQ3’s strength lies in how it protects future messages through ratcheting:
- Symmetric Ratchet: Each message gets a unique key derived from the current state. This ensures that older messages can’t be decrypted even if the main key is compromised later (forward secrecy).
- ECDH Ratchet: Fresh elliptic curve keys are periodically exchanged, introducing new secrecy into the session. This means adversaries can’t decrypt new messages even if they get hold of old keys (post-compromise security).
- Kyber Ratchet: While resource-intensive, a Kyber key exchange is included conditionally. This safeguards against quantum attacks designed to break all past keys if one is obtained.
- Adaptive Rekeying: To balance security and bandwidth, the expensive Kyber ratchet runs less often. iMessage cleverly adjusts the frequency based on message count, time elapsed, and network conditions, with software updates allowing for even quicker rekeying as needed.
Message Encryption
- Padding: PQ3 uses the efficient Padmé heuristic to pad messages before encryption, minimizing metadata leakage about message length.
- Encryption: Standard, but quantum-resistant, AES-CTR encryption protects the padded message for data confidentiality.
Authentication
- Continuous Verification: Each message is digitally signed using ECDSA, with the signature bound to your iMessage keys. This prevents tampering and impersonation.
- Contact Key Verification (CKV): If enabled, this further strengthens security by confirming that device keys match what’s stored in your iCloud Keychain.
Wrapping Up
PQ3’s sophisticated integration of quantum-resistant protocols and continuous rekeying makes it unmatched in secure messaging today. Its hybrid design wisely balances security and practicality. iMessage, once again, demonstrates its commitment to user privacy and positions itself as a global leader in the fight against emerging quantum threats.
FAQs
- When will PQ3 be available? PQ3 will arrive with iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, macOS 14.4, and watchOS 10.4. Developer previews might have it sooner.
- Will my old messages be secure? PQ3 automatically protects new conversations, old ones won’t be retroactively protected.
- Is my phone powerful enough? iMessage is optimized, and PQ3’s impact should be unnoticeable on modern devices.
- Does this mean perfect security? No system is unbreakable, but PQ3 makes iMessage incredibly hard to attack, even by future technology.
- Will other apps catch up? PQ3 sets a high standard. It may take time for others to develop comparable solutions.
For an even deeper dive, check out Apple’s official blog post.
Tony has a bachelor’s degree from the University of Phoenix and over 11 years of writing experience between multiple publications in the tech, photography, lifestyle, and deal industries.











Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!